5 New Features in PHP 7
The PHP people group is VERY eager to welcome this most recent
discharge. However, that doesn't mean PHP has been dormant this time. Despite what might be expected, minor arrivals of PHP 5 conveyed many energizing highlights to PHP, including backing of Object-Oriented programming and numerous highlights related with that.
All in all, for one thing, why 7 and not 6? Allows simply say, unicode turned out poorly well. Likewise with numerous activities, prerequisites were not all around characterized and individuals couldn't concede to things, so the undertaking came to a standstill.
Other than unicode, for encoding exceptional and global characters, every one of the highlights being talked about for PHP 6 were in the long run executed in PHP 5.3 and later, so we truly didn't miss whatever else. Through everything, numerous things were found out and another procedure for include demands was set up. At the point when the list of capabilities for a noteworthy discharge was acknowledged, it was chosen, to dodge disarray with a dead venture, and to skip to variant 7 for the most recent discharge.
So what makes PHP 7 so extraordinary? What does this mean for you as a designer?
We'll investigate the best 5 includes here. In the event that you'd like a more profound jump, look at my workshop, Introduction to PHP7, or my course, Build a Basic PHP Website. php training in chandigarh

1. SPEED!
The engineers worked hard to refactor the PHP codebase to lessen memory utilization and increment execution. What's more, they positively succeeded.
Benchmarks for PHP 7 reliably indicate speeds twice as quick as PHP 5.6 and ordinarily much quicker! Despite the fact that these outcomes are not ensured for your task, the benchmarks were tried against significant activities, Drupal and WordPress, so these numbers don't originate from unique execution tests.
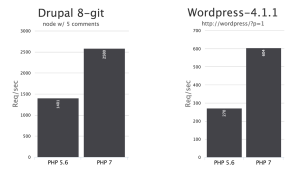
With measurements that show 25% of the web being kept running on WordPress, this is an awesome thing for everybody.
2. Type Declarations
Sort announcements just means determining which kind of factor is being set as opposed to enabling PHP to set this naturally. PHP is thought to be a powerless composed dialect. Generally, this implies PHP does not expect you to pronounce information composes. Factors still have information composes related with them however you can do radical things like adding a string to a number without bringing about a blunder. Sort revelations can enable you to characterize what ought to happen so you get the normal outcomes. This can likewise make your code less demanding to peruse. We'll take a gander at some particular illustrations presently.
Since PHP 5, you can utilize type indicating to determine the normal information kind of a contention in a capacity affirmation, however just in the assertion. When you call the capacity, PHP will check regardless of whether the contentions are of the predefined compose. If not, the run-time will raise a blunder and execution will be ended. Other than just being utilized as a part of capacity presentations, we were likewise restricted to fundamentally 2 composes. A class name or a cluster.
Here’s an example:
function enroll(Student $student, array $classes) {
foreach ($classes as $class) {
echo "Enrolling " . $student->name . " in " . $class;
}
}
enroll("name",array("class 1", "class 2")); // Catchable fatal error: Argument 1 passed to enroll() must be an instance of Student, string given
enroll($student,"class"); // Catchable fatal error: Argument 2 passed to enroll() must be of the type array, string given
enroll($student, array("class 1", "class 2"));
If we somehow happened to make a capacity for enlisting understudies, we could necessitate that the primary contention be a question of the understudy class and the second contention to be a variety of classes. In the event that we endeavored to pass only the name rather than a question we would get a deadly blunder. If we somehow managed to pass a solitary class rather than a cluster, we would likewise get a mistake. We are required to pass an understudy protest and a cluster.
function stringTest(string $string) {
echo $string;
}
stringTest("definitely a string");
If we somehow happened to endeavor to check for a scalar variable, for example, a string, PHP 5 anticipates that it will be a protest of the class string, not the variable kind string. This implies you'll get a Fatal mistake: Argument 1 go to stringTest() must be an occurrence of string, string given.
Scalar Type Hints
With PHP7 we currently have included Scalar composes. In particular: int, buoy, string, and bool.
By including scalar make demonstrates and engaging strict necessities, it is assumed that all the more right and self-chronicling PHP ventures can be formed. It furthermore gives you more control over your code and can make the code less requesting to examine.
As per usual, scalar make proclamations are non-strict, which infers they will attempt to change the main sort to organize the sort shown by the sort attestation. By the day's end, if you pass a string that starts with a number into a limit that requires a float, it will grab the number from the most punctual beginning stage and oust everything else. Passing a float into a limit that requires an int will advance toward getting to be int(1).

Strict Example
function getTotal(float $a, float $b) {
return $a + $b;
}
getTotal(2, "1 week");
// int(2) changed to float(2.0) and string “1 week” changed to float(1.0) but you will get a “Notice: A non well formed numeric value encountered”
//returns float(3)
Get Total(2.8, "3.2");
// string "3.2" changed to float(3.2) no notice
//returns float(6)
getTotal(2.5, 1);
// int(1) changed to float(1.0)
//returns float(3.5)The getTotal work gets 2 buoys and includes them together while it restores the aggregate.
Without strict kinds turned on, PHP endeavors to cast, or change, these contentions to coordinate the sort indicated in the capacity.
So when we call getTotal with non-strict composes utilizing an int of 2 and a string of "multi week", PHP changes over these to coasts. The principal contention would be changed to 2.0 and the second contention would be changed to 1.0. In any case, you will get a Notice: since this is certainly not an all around framed numeric esteem. It will then restore an estimation of 3. Which would be totally wrong in the event that we were attempting to include days.
When we call getTotal with the buoy 2.8 and the string of "3.2", PHP changes over the string into the buoy 3.2. with no notice since it was a smooth transformation. It at that point restores an estimation of 6 When we call getTotal with non-strict composes utilizing the buoy 2.5 and the whole number 1. The whole number gets changed over to the buoy 1.0 and the capacity returns 3.5
Strict Example
Moreover, PHP 7 gives us the chance to empower strict mode on a record by document premise. We do this by declare(strict_types=1); at the highest point of any given document. This MUST be the specific first line, even before namespaces. Announcing strict composing will guarantee that any capacity calls made in that document entirely hold fast to the sorts indicated.
Moreover, PHP 7 gives us the chance to empower strict mode on a record by document premise. We do this by declare(strict_types=1); at the highest point of any given document. This MUST be the specific first line, even before namespaces. Announcing strict composing will guarantee that any capacity calls made in that document entirely hold fast to the sorts indicated.
Strict is controlled by the record in which the call to a capacity is made, not the document in which the capacity is characterized.
On the off chance that a sort statement crisscross happens, a "Deadly Error" is tossed and we realize that something isn't working as wanted, rather than enabling PHP to just speculate what we need to happen, which can make apparently arbitrary and hard analyze issues. We'll take a gander at getting and dealing with blunders in the following area. Yet, until further notice, we should take a gander at a case utilizing strict composes turned on.
declare(strict_types=1);
function getTotal(float $a, float $b) {
return $a + $b;
}
getTotal(2, "1 week");
// Fatal error: Uncaught TypeError: Argument 2 passed to getTotal() must be of the type float, string given
Get Total(2.8, "3.2");
// Fatal error: Uncaught TypeError: Argument 2 passed to getTotal() must be of the type float, string given
getTotal(2.5, 1);
// int(1) change to float(1.0)
//returns float(3.5)
At the point when the proclaim strict_type has been turned on, the initial two considers that pass a string will create a Fatal blunder: Uncaught TypeError: Argument 2 go to getTotal() must be of the sort coast, string given.
The special case to strict composing with appeared in the third call. In the event that you pass an int as a contention that is searching for a buoy, PHP will perform what is designated "augmenting", by including .0 to the end and the capacity returns 3.5
Return Type Declarations
PHP 7 likewise bolsters Return Type Declarations which bolster all an indistinguishable sorts from contentions. To indicate the arrival compose, we include a colon and after that the sort just before the opening wavy section.
work getTotal(float $a, coast $b) : glide {
On the off chance that we determine the arrival kind of buoy, it will work precisely like it has been in the past 2 cases since the sort being returned was at that point a buoy. Including the arrival compose enables you to make sure your capacity returns what is normal and additionally making it simple to see forthright how the capacity functions.
Non-strict int
In the event that we indicate the arrival compose as int without strict sorts set, everything will work the same as it managed without an arrival compose, the main contrast is that it will drive the arrival to be an int. In the third call the arrival esteem will truncate to 3 on the grounds that the coasting point will be dropped
function getTotal(float $a, float $b) : int {
return $a + $b;
}
getTotal(2, "1 week");
// changes int(2) to float(2.0) & string(“1 more”) to float(1.0)
// returns int(3);
getTotal(2.8, "3.2");
// changes string "3.2" to float(3.2)
// returns int(6)
getTotal(2.5, 1);
// changes int(1) to float(1.0)
// returns int(3)
Strict int
On the off chance that we turn strict composes on, we'll get a Fatal mistake: Uncaught TypeError: Return estimation of getTotal() must be of the sort number, coast returned. For this situation we'll have to explicitly give our arrival esteem a role as an int. This will at that point restore the truncated esteem.
declare(strict_types=1);
function getTotal(float $a, float $b) : int {
// return $a + $b;
// Fatal error: Uncaught TypeError: Return value of getTotal() must be of the type integer, float returned
return (int)($a + $b); // truncate float like non-strict
}
getTotal(2.5, 1); // changes int(1) to float(1.0) and returns int(3)
Why?
The new Type Declarations can make code less demanding to peruse and powers things to be utilized as a part of the manner in which they were expected. A few people want to utilize unit testing to check for proposed use. Having computerized tests for your code is exceptionally suggested, yet you can utilize both unit tests and Type Declarations. In any case, PHP does not expect you to proclaim composes but rather it can make code less demanding to peruse. You can see comfortable beginning of a capacity, what is required and what is returned.
3. Error Handling
The following element we going to cover are the progressions to Error Handling. Taking care of lethal mistakes in the past has been beside outlandish in PHP. A deadly blunder would not conjure the mistake handler and would basically stop your content. On a creation server, this for the most part implies demonstrating a clear white screen, which confounds the client and makes your validity drop. It can likewise cause issues with assets that were never shut legitimately are still being used or even bolted.
In PHP 7, an exemption will be tossed when a deadly and recoverable blunder happens, as opposed to simply halting the content. Deadly blunders still exist for specific conditions, for example, coming up short on memory, and still carry on as before by quickly halting the content. An uncaught exemption will likewise keep on being a deadly blunder in PHP 7. This implies if a special case tossed from a blunder that was deadly in PHP 5 goes uncaught, it will even now be a lethal mistake in PHP 7.
I need to bring up that different sorts of mistakes, for example, alerts and notification stay unaltered in PHP 7. Just lethal and recoverable blunders toss exemptions.
In PHP 7, Error and Exception both execute the new Throwable class. This means they essentially work a similar way. And furthermore, you would now be able to utilize Throwable in attempt/get squares to get both Exception and Error objects. Keep in mind that it is better practice to get more particular special case classes and handle each as needs be. Be that as it may, a few circumstances warrant getting any special case, (for example, for logging or system mistake dealing with). In PHP 7, these catch-all squares should get Throwable rather than Exception.
New Hierarchy
|- Exception implements Throwable
|- …
|- Error implements Throwable
|- TypeError extends Error
|- ParseError extends Error
|- ArithmeticError extends Error
|- DivisionByZeroError extends ArithmeticError
|- AssertionError extends Error
The Throwable interface is actualized by both Exception and Error. Under Error, we currently have some more particular blunder. TypeError, ParseError, A couple math blunders and an AssertionError.
Throwable Interface
On the off chance that Throwable was characterized in PHP 7 code, it would resemble this
interface Throwable
{
public function getMessage(): string;
public function getCode(): int;
public function getFile(): string;
public function getLine(): int;
public function getTrace(): array;
public function getTraceAsString(): string;
public function getPrevious(): Throwable;
public function __toString(): string;
}
In the event that you've worked with Exceptions by any means, this interface should look commonplace. Throwable determines techniques almost indistinguishable to those of Exception. The main contrast is that Throwable::getPrevious() can restore any occasion of Throwable rather than only an Exception.
This is what a straightforward catch-all square resembles:
try {
// Code that may throw an Exception or Error.
} catch (Throwable $t) {
// Executed only in PHP 7, will not match in PHP 5
} catch (Exception $e) {
// Executed only in PHP 5, will not be reached in PHP 7
}
To get any special case in PHP 5.x and 7 with a similar code, you would need to include a catch hinder for Exception AFTER getting Throwable first. When PHP 5.x help is never again required, the square getting Exception can be expelled.
Essentially all blunders in PHP 5 that were lethal, now toss occurrences
of Error in PHP 7
.
Sort Errors
A TypeError event is hurled when a limit conflict or return regard does not facilitate a sort disclosure. In this limit, we've demonstrated that the dispute should be an int, anyway we're going in strings that can't be changed over to ints. So the code will hurl a TypeError.
function add(int $left, int $right) {
return $left + $right;
}
try {
echo add('left','right');
} catch (\TypeError $e) {
// Log error and end gracefully
echo $e->getMessage(), "\n";
// Argument 1 passed to add() must be of the type integer, string given
}
This could be utilized for adding transportation and dealing with to a shopping basket. On the off chance that we passed a string with the delivery transporter name, rather than the transportation cost, our last aggregate would not be right and we would risk losing cash on the deal.

Parse Errors
A Parse Error is tossed when an included/required record or eval()'d code contains a linguistic structure blunder. In the principal attempt we'll get a Parse Error since we called the vague capacity var_dup rather than var_dump. In the second attempt, we'll get a Parse Error on the grounds that the required record has a language structure blunder.
try {
$result = eval("var_dup(1);");
} catch (\Error $e) {
echo $e->getMessage(), "\n";
//Call to undefined function var_dup()
}
try {
require 'file-with-parse-error.php';
} catch (Parse Error $e) {
echo $e->getMessage(), "\n";
//syntax error, unexpected end of file, expecting ',' or ';'
}
Suppose we check if a client is signed in, and assuming this is the case, we need to incorporate a record that contains an arrangement of route joins, or an uncommon offer. In the event that there is an issue with that incorporate record, getting the ParseError will enable us to inform somebody that that document should be settled. Without getting the ParseError, the client may not know they are missing something.
4. New Operators
Spaceship Operator
PHP 7 likewise presents to us some new administrators. The first we will investigate is the spaceship administrator. With a name that way, who wouldn't like to utilize it? The spaceship administrator, or Combined Comparison Operator, is a pleasant expansion to the dialect, supplementing the more prominent than and not as much as administrators.
Spaceship Operator
< = >
$compare = 2 <=> 1
2 < 1? return -1
2 = 1? return 0
2 > 1? return 1
The spaceship administrator is assembled utilizing three individual administrators, not as much as, rise to, and more prominent than. Basically what it does is check the every administrator separately. To start with, not exactly. On the off chance that the incentive on the left is not as much as the incentive on the right, the spaceship administrator will return - 1. If not, it will proceed onward to test if the incentive on the left is EQUAL to the incentive on the right. Provided that this is true, it will return 0. If not it will proceed onward to the last test. On the off chance that the incentive on the left is GREATER THAN the incentive on the right. Which, if the other 2 haven't passed, this one must be valid. What's more, it will return 1.
 PHP training Institute -
PHP training Institute -
If you are looking best
php training in chandigarh than join cbitss technologies .
CBitss Technologie Provides training in chandigarh ,..more information visit website .
The most common usage for this
operator is in sorting.
Invalid Coalesce Operator
Another new administrator, the Null Coalesce Operator, is adequately the mythical if-set-or. It will restore the left operand on the off chance that it isn't NULL, else it will restore the right. The critical thing is that it won't raise a notice if the left operand is a non-existent variable.
$name = $firstName ?? "Visitor";
For instance, name squares with the variable firstName, twofold question marks, the string "Visitor".
In the event that the variable firstName is set and isn't invalid, it will relegate that incentive to the variable name. Or on the other hand else it will allot "Visitor" the variable name.
Prior to PHP 7, you could compose something like
on the off chance that (!empty($firstName)) $name = $firstName;
else $name = "Visitor";
What makes this considerably more great, is that you can stack these! This activity will check every thing from left to right and when if discovers one that isn't invalid it will utilize that esteem.
$name = $firstName ?? $username ?? $placeholder ?? "Visitor";
This administrator searches unequivocally for invalid or does not exist. It will get an unfilled string.
5. Simple User-arrive CSPRNG
What is Easy User-land CSPRNG?
Invalid Coalesce Operator
Another new administrator, the Null Coalesce Operator, is adequately the mythical if-set-or. It will restore the left operand on the off chance that it isn't NULL, else it will restore the right. The critical thing is that it won't raise a notice if the left operand is a non-existent variable.
$name = $firstName ?? "Visitor";
For instance, name squares with the variable firstName, twofold question marks, the string "Visitor".
In the event that the variable firstName is set and isn't invalid, it will relegate that incentive to the variable name. Or on the other hand else it will allot "Visitor" the variable name.
Prior to PHP 7, you could compose something like
on the off chance that (!empty($firstName)) $name = $firstName;
else $name = "Visitor";
What makes this considerably more great, is that you can stack these! This activity will check every thing from left to right and when if discovers one that isn't invalid it will utilize that esteem.
$name = $firstName ?? $username ?? $placeholder ?? "Visitor";
This administrator searches unequivocally for invalid or does not exist. It will get an unfilled string.
5. Simple User-arrive CSPRNG
$bytes = random_bytes(5); // length in bytes
var_dump(bin2hex($bytes));
// output similar to: string(10) "385e33f741"
These are bytes not whole numbers. On the off chance that you are hoping to restore an arbitrary number, or whole number, you should utilize the random_int work.
Irregular Int
When utilizing random_int you supply 2 contentions, min and max. This is the base and most extreme numbers you need to utilize.
For instance:-
random_int(1,20);
Would restore an arbitrary number somewhere in the range of 1 and 20, including the likelihood of 1 and 20.
*If you are utilizing the rand work for anything even remotely secure, you'll need to change the rand capacity to random_int.








